 A fabled monster, usually having the head and wings of an
eagle and the body of a lion.
A fabled monster, usually having the head and wings of an
eagle and the body of a lion.
All definitions are taken from Webster's Encyclopedic Unabridged Dictionary of the English Language, unless otherwise specified.
Griffin, Gryphon or Griffon (grif-in) Classical Mythology
 A fabled monster, usually having the head and wings of an
eagle and the body of a lion.
A fabled monster, usually having the head and wings of an
eagle and the body of a lion.
Hippogriff (hip-o-grif) Classical Mythology
A fabulous creature resembling a griffin but having the body and hind parts
of a horse.
Manticore (man-ti-kor)
Not in Dictionary. "The Manticore lives in the Indies. It has the body of
a lion, a spiked tail with the sting of a scorpion, a man's head with three
rows of teeth and gleaming, blood-red eyes. Its shrill voice sounds much
like a flute. It is very powerful and can jump great distances. It is a
ravenous beast, particularly fond of human flesh."
(Mythical Beasts Coloring Book, by Fridolf Johnson, Dover Publications, 1976)
Gorgon (gor-gon) Classical Mythology
Any of three sister monsters, Stheno, Euryale, and Medusa, commonly
represented as having snakes for hair, wings, brazen claws, and eyes that
turned anyone looking into them to stone. Medusa, the only mortal Gorgon,
was beheaded by Perseus.
Medusa (me-doo-sa) Classical Mythology
The only mortal of the three Gorgons. She was killed by Perseus, and her
head was mounted upon the aegis of Zeus and Athena.
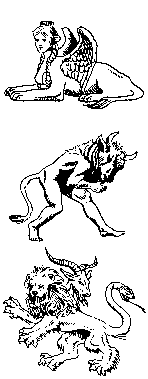 Sphinx (sfingks) Egyptian/Classical Mythology
Sphinx (sfingks) Egyptian/Classical Mythology
Literally-"She who holds (her victims) fast."
1. A figure of an imaginary creature having the head of a man or an animal
and the body of a lion.
2. A monster, daughter of Echidna, usually represented as having the head
and breast of a woman, the body of a lion, and the wings of an eagle.
Seated on a rock outside Thebes, she proposed a riddle to travelers,
killing them when they answered incorrectly, as all did before Oedipus.
When he answered her riddle correctly the Sphinx killed herself.
3. Any similar monster.
Minotaur (min-o-tar) Classical Mythology
A monster, the offspring of Pasiphae and the Cretan bull, that had the
head of a bull on the body of a man: housed in the Cretan Labyrinth, it
was fed on human flesh until Theseus, helped by Ariadne, killed it.
Chimera or Chimaera (chi-mer-ah)
1. A mythological fire-breathing monster, commonly represented with a
lion's head, a goat's body, and a serpent's tail.
2. Any similarly grotesque monster having disparate parts, especially as
depicted in decorative art.
Cockatrice (kok-a-tris)
A legendary monster with a deadly glance, supposedly hatched by a serpent
from the egg of a cock, and commonly represented with the head, legs and
wings of a cock and the body and tail of a serpent.
Basilisk (bas-a-lisk) Classical Mythology
A creature, variously described as a serpent, lizard, or dragon, said to
kill by its breath or look.
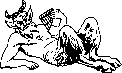 Satyr (sat-er) Classical Mythology
Satyr (sat-er) Classical Mythology
One of a class of woodland deities, attendant on Bacchus, represented as
part human and part goat and noted for riotousness and lasciviousness.
Pan was a well known Satyr.
 Mythic Images of Pan
Mythic Images of Pan
 The Great God Pan
The Great God Pan
 Myth Man's Homework Helper: Pan
Myth Man's Homework Helper: Pan
Cerberus (ser-ber-us) Classical Mythology
A dog, usually represented as having three heads, which guarded the
entrance of the infernal regions.
Lamia (la-mee-a) Classical Mythology
One of a class of fabulous monsters, commonly represented with the head and
breast of a woman and the body of a serpent, said to allure youths and
children in order to suck their blood.
